货号:CK17
细胞活性/毒性双重检测试剂盒
Viability/Cytotoxicity Multiplex Assay Kit
储存条件:0-5度保存
运输条件:室温
特点:
-
- CCK-8与LDH双指标检测毒性,数据更全面。
- 准备1次细胞,同时检测2项数据。
- 内含500T的CCK-8与LDH检测试剂盒,
- 价格优于单独购买。
选择规格:500 tests
关联产品
NO.1. ROS Assay Kit -Highly Sensitive DCFH-DA- ROS检测
NO.2. Annexin V, FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit 细胞凋亡检测
NO.3. Calcein-AM/PI Double Staining Kit 活死细胞双染检测
NO.4. Cell Cycle Assay Kit 细胞周期检测
NO.5. Caspase-3 Assay Kit-Colorimetric- 细胞凋亡检测
试剂盒内含
500 tests Dye Mixture 5mlX1
[500 tests]
.WST-8,1-Methoxy PMS混合液
Cytotoxicity LDH Assay Kit-WST
[500 tests]
.Dye Mixture X1
.Assay Buffer 15.5mlX1
.Lysis Buffer 155mlX1
.Stop Solutin 27.5mlX1
产品概述

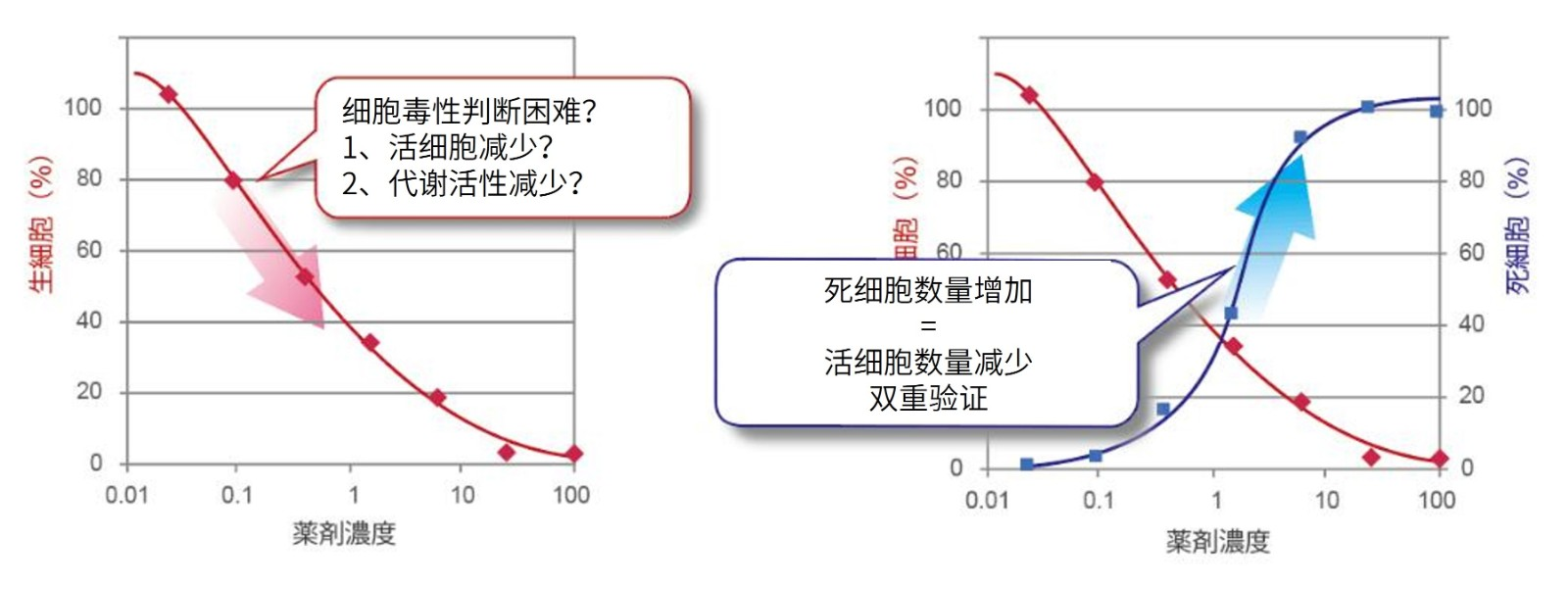
细胞毒性检测通常通过检测活细胞数量或者死细胞数量来确定。而为了更加全面的评价细胞毒性情况,多种评价方法相互验证的需求与日俱增。Viability/CytotoxicityMultiplex Assay Kit可以综合评价细胞毒性。试剂盒内含Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) 和Cytotoxicity LDH Assay Kit-WST® (LDH Assay Kit),分别用于测定活细胞和死细胞数量。
CCK-8通过检测活细胞中脱氢酶活性来确定活细胞数,而LDH Assay Kit通过检测受损细胞膜释放LDH的量来确定死细胞数。LDH Assay Kit可以直接添加到含有细胞的培养基中检测 (一步法)。也可以分离细胞后,加到细胞培养基上清液中检测 (低损伤法,分离的细胞可以做其它实验)。两种细胞毒性评价指标,CCK-8和LDH Assay Kit(低损伤法) 可以使用同一批细胞同时进行实验。
产品特点
不同细胞毒性指标,双重印证。增加结果可信性。
单独检测CCK-8,细胞毒性判断不准确
1、单纯检测活细胞数量(CCK-8、MTT、MTS、XTT等)
2种指标一起检测,增加数据准确性
1、单纯检测活细胞数量(CCK-8、MTT、MTS、XTT等)
2、活细胞检测+死细胞检测(细胞膜损伤)
检测原理
LDH Assay Kit:细胞膜损伤,LDH外漏,通过检测LDH活性判断细胞毒性。
CCK-8:可以使用NADH作为指标来确认活细胞中的代谢活性。

同时检测的操作方法

本试剂盒包括用于测量活细胞的CCK-8和用于测量死细胞的LDH分析试剂盒,两者均可通过平板分析法在相同的吸收波长下进行评估。 此外,同一细胞样本可用于同时评估活细胞和死细胞,从而节省了时间和精力。
性价比高
本产品作为CCK-8(500 tests)与Cytotoxicity LDH Assay Kit(500 tests)组合套装,低于单独购买的总价。适合新接触细胞毒性检测的用户,用于前期摸索实验条件。单独产品链接见下方。大包装购买,单价会降低很多。
Cell Counting Kit-8
Cytotoxicity LDH Assay Kit-WST
参考文献
1. Integrated Omics Reveals Tollip as an Regulator and Therapeutic Target for Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Mice,
Hepatology., 2019, doi: 10.1002/hep.30705
2. Amplified Cancer Immunotherapy of Surface Engineering Antigenic Microparticles Vaccine by Synergistically Modulating Tumor
Microenvironment, ACS Nano, 2019, 13, 11, 12553-12566
3. A novel IFNα-induced long noncoding RNA negatively regulates immunosuppression by interrupting H3K27 acetylation in head
and neck squamous cell carcinoma, Molecular Cancer, 2020,19, 4, doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1123-y
4. Untangling the co-effects of oriented nanotopography and sustained anticoagulation in a biomimetic intima on neovessel
remodeling, Biomaterials, 2019, 119654
5. In Vitro and in Vivo Analysis of Mineralized Collagen-Based Sponges Prepared by a Plasma- and Precursor-Assisted
Biomimetic Process, ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9, 27, 22185-22194
6. MoS2-LA-PEI nanocomposite carrier for real-time imaging of ATP metabolism in glioma stem cells co-cultured with
endothelial cells on a microfluidic system, Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2018, 99, 142-149
7. Biocompatible carbon nanotube fiber for implantable supercapacitors, Carbon, 2017, 122, 162-167
8. Genomic sequencing and editing revealed the GRM8 signaling pathway as potential therapeutic targets of squamous cell
lung cancer, Cancer Letters, 2019, 442, 53-67
9. Knockdown of TGF-β1 expression in human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells reverts their exosome-mediated EMT
promoting effect on lung cancer cells, Cancer Letters, 2018, 428:34-44
10. Restriction of exogenous DNA expression by SAMHD1, Science Bulletin, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2019.12.028
11. PARP1 inhibition alleviates injury in ARH3-deficient mice and human cells, JCI Insight, 2019, 4(4), e124519
12. Downregulation of MCL-1 and upregulation of PUMA using mTOR inhibitors enhance antitumor efficacy of BH3 mimetics in
triple-negative breast cancer, Cell Death & Disease, 2018, 9(2), 137
13. Ischemic preconditioning attenuates ischemia/reperfusion-induced kidney injury by activating autophagy via the SGK1
signaling pathway, Cell Death & Disease, 2018, 9, 338
14. Pathological Endogenous a-Synuclein Accumulation in Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cells Potentially Induces Inclusions in
Multiple System Atrophy, Stem Cell Reports, 2018, 10(2), 356-365
15. PDH-mediated metabolic flow is critical for skeletal muscle stem cell differentiation and myotube formation during regeneration
in mice, FASEB Journal, 2019, 33(7), 8094-8109
16. Benzo[a]pyrene-decreased gap junctional intercellular communication via calcium/calmodulin signaling increases apoptosis in
TM4 cells, Journal of Applied Toxicology, 2018, 38(8), 1091-1103

