Phanta® HS Super-Fidelity DNA Polymerase,热启动版高保真DNA聚合酶,扩增速度是常规聚合酶的4-150 倍,
Phanta HS Super-Fidelity DNA Polymerase
2022-04-23 17:10:00
2022-04-23 17:10:00
Phanta® HS Super-Fidelity DNA Polymerase,热启动版高保真DNA聚合酶,扩增速度是常规聚合酶的4-150 倍,
Cosmo Bio抗体,Cosmo Bio,Anti des-pyroGlu-Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone II (GnRH II/LH-RH II) pAb (Rabbit, Antiserum),CAC-KZ-HS-P04
Application: IHC, Neutralization, RIA
Clonality: Polyclonal
Host: Rabbit
Purification: Serum
Reactivity: Vertebrates, Chicken
Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone (GnRH), also known as Luteinizing-hormone-releasing-hormone (LHRH) and luliberin, is a tropic peptide hormone responsible for the release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and Luteinizing Hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary. GnRH is synthesized and released from neurons within the hypothalamus. The peptide belongs to gonadotropin-releasing hormone family.
Cosmo Bio抗体,Cosmo Bio,Anti Bovine Milk Exosome pAb (Rabbit, Ammonium Sulfate Purified),CAC-EXO-AB-01
Application: WB
Clonality: Polyclonal
Host: Rabbit
Purification: Ammonium Sulfate
Reactivity: Bovine
Exosomes are membrane vesicles with a diameter of about 50 nm to 150 nm. They are secreted by most cells and are observed in body fluids such as saliva, blood, urine, amniotic fluid and malignant ascites. By encapsulating miRNA, mRNA, protein, micro peptides exosomes may be responsible for transmitting information to target cells or tissues.(1) It is known that cancer metastasis can be suppressed by neutralizing exosome signaling with antibodies specific for exosome surface antigens such as CD9 and CD63.(2) Exosomes are also present in the milk of a wide range of animals such as humans, cows and rats.(3) Furthermore, recent studies have demonstrated the utility of exosomes derived from raw milk as a means of orally administering anticancer agents.(4)
References:
1) Hoshino A, et al. (2015) Tumour exosome integrins determine organoorganic metabolism. Nature. 527(7578):329-35.
2) Nao Nishida-Aoki, et al. (2017) Disruption of Circulating Extracellular Vesicles as a Novel Therapeutic Strategy against Cancer Metastasis. Mol Ther. 25(1):181-191.
3) Hirohisa Izumi, et al. (2015) Bovine milk exosomes contain microRNA and mRNA and is taken up by human macrophages.
4) Ashish K. Agrawal et al. (2017) Milk-derived exosomes for oral delivery of paclitaxel. Nanomedicine. 13(5):1627-1636.
Cosmo Bio抗体,Cosmo Bio,Anti Acetylaminofluorene (AAF) DNA Adducts mAb (Clone AAF-1),CAC-NM-MA-001
Application: ICC, ELISA, IHC, IF
Clonality: Monoclonal
Host: Mouse
Purification: Ammonium Sulfate
Reactivity: All
DNA adducts in mammalian cells exposed to N-acetoxy-2-acetylaminofluorene (NA-AAF), an activated derivative of the potent carcinogen 2-AAF, play significant roles in cell killing, chromosome aberration, gene mutation and neoplastic transformation. NA-AAF binds covalently to guanine in the DNA of mammalian cells and produces three different DNA adducts. The C-8 adducts dG-C8-AAF and deacetylated dG-C8-AF account for the major portion of the DNA-bound products, while the minor N2 adduct dG-N2-AAF accounts for the remainder. The relative induction levels of the two major C-8 adducts vary among cell types. These adducts distort the DNA helix and therefore are repaired by nucleotide excision repair in human cells. Our AAF-1 antibodies bind most efficiently to dG-C8-AAF and less efficiently to dG-C8-AF in denatured DNA. The antibodies enable one to detect AAF-DNA adducts in DNA from cultured cells using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and to visualize them in cultured cells or rodent tissues by immunofluorescence (IF). This technology will contribute to understanding of molecular mechanisms in AAF-related research fields including cancer research, anticancer research and toxicology.
Source: Toshio Mori Professor, Research Institute for Advanced Medicine, Nara Medical University.
References:
1) R.H. Heflich and R.E. Neft, Genetic toxicity of 2-acetylaminofluorene, 2-aminofluorene and some of their metabolites and model metabolites. Mutation Res. 318 (1994) 73-174.
2) E.Kriek, Fifty years of research on N-acetyl-2-aminofluorene, one of the most versatile compounds in experimental cancer research. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 118 (1992) 481-489.
3) T. Iwamoto et al., In situ detection of acetylaminofluorene-DNA adducts in human cells using monoclonal antibodies. DNA Repair 3 (2004) 1475-1482.
产品介绍 产品介绍 相关方案 全部规格 全部规格 产品介绍 硅碳棒铝编织带由铝丝经编织机编织成椭圆状管网,通过设备拉伸压扁制作,柔软度好,易散热,耐弯曲,导电率强,两端或一端由铝管接头压制,再经打孔制成。硅碳棒编织带有单层单孔或双孔,双层单孔或双孔,多层或加厚或加长,可根据需求订做一定长度,孔径或宽度,层数等,欢迎咨询 选择夹具要选择与硅碳棒直径相匹配的夹子,避免夹持松动;接线后要认真检查连接带与棒接触是否牢固,若接触不良通电后会造成打弧现象,使整支棒报废。连接带有铝编织连接带,铝箔连接带,是用来导电的;外面的夹子只起夹紧作用,不用来导电。安装元件棒时夹头上的螺丝不要一次拧的太紧,而且用力要自然,避免将外力施加到棒体上,待元件棒升到高温时再次拧紧,因为这时棒有一定塑性不易折断。连接带的末端与母线联结。为了避免应力传到元件上,连接带长度应略大于元件和母线间的直线距离,至少20mm余量。元件夹头部分温度一般不要高于200度,否则会影响夹头使用寿命。电炉后期使用中也要定期检查夹头部位是否接触良好,以便及时调整。固定夹块,整个元件的重量都是由它承担,元件的位置也由它决定。安装时使元件垂直悬挂。 全部规格 16*200铝编织带 实验室直径12mm600长硅碳棒直棒接线带 16*200
Cosmo Bio抗体,Cosmo Bio,Anti Alpha Synuclein (9 Antibody Set) pAb (Rabbit, Antiserum),CAC-TIP-SN-SET
Application: IHC, WB, ELISA
Clonality: Polyclonal
Host: Rabbit
Purification: Serum
Reactivity: Human, Mouse
Neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease have been increasing rapidly and have become a serious social problem. In recent years, new causative genes have been discovered for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and other intractable neurological diseases opening new avenues for research on pathogenesis. It has been suggested that aggregation and accumulation of specific proteins cause neurotoxicity and the formation of lesions, but the onset and progression mechanisms are still unclear. Neuropathological diagnostic and experimental model biomarkers are needed for drug construction, drug discovery, and therapeutic development.
Alpha-Synuclein, a 140-amino acid protein abundantly expressed in presynaptic terminals, is a component of intraneuronal or glial inclusions observed in cases of Parkinson’s disease (PD), Dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) and Multiple system atrophy (MSA). Although alpha-synuclein is a natively unfolded protein, fibrillization or conformational change(s) of alpha-synuclein is central to the pathogenesis of alpha-synucleinopathies. The amino-terminal region of alpha-synuclein consists of seven imperfect repeats, each 11 amino acids in length, with the consensus sequence KTKEGV. The repeats partially overlap with a hydrophobic region (amino acids 61-95). The carboxy-terminal region (amino acids 96-140) is negatively charged. These antibodies are powerful tools for biochemical and IHC analyses of neurodegenerative diseases and for evaluation of conformational changes of alpha-synuclein.
References:
1) Masami Masuda et al., Inhibition of a-synuclein fibril assembly by small molecules: Analysis using epitope-specific antibodies. FEBS Letters (2009) 583, 787-791. PMID 19183551
2) Motokuni Yonetani et al., Conversion of wild-type alpha-synuclein into mutant-type fibrils and its propagation in the presence of A30P mutant. Journal of Biological Chemistry (2009) 284, 7940-7950. PMID 19164293
Cosmo Bio抗体,Cosmo Bio,Anti NG2 (CSPG4) mAb (Clone 2161D7),CAC-PRPG-NG-M01
Application: FC, ELISA, IHC(p), WB, IP, ICC
Clonality: Monoclonal
Host: Mouse
Purification: Supernatant
Reactivity: Human
Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 4, also known as melanoma-associated chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan (MCSP) or neuron-glial antigen 2 (NG2), is a chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan that in humans is encoded by the CSPG4 gene. CSPG4 plays a role in stabilizing cell-substratum interactions during early events of melanoma cell spreading on endothelial basement membranes. It represents an integral membrane chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan expressed by human malignant melanoma cells. CSPG4/NG2 is also a hallmark protein of oligodendrocyte progenitor cells (OPCs) and OPC dysfunction has been implicated as a candidate pathophysiological mechanism of familial schizophrenia. A research group investigating the role of genetics in schizophrenia, reported, two rare missense mutations in CSPG4 gene, segregating within families (CSPG4A131T and CSPG4V901G mutations). The researchers also demonstrated that induced pluripotent stem cells(iPSCs)-derived OPCs from CSPG4A131T mutation carriers exhibited abnormal post-translational processing, subcellular localization of the mutant NG2 protein, aberrant cellular morphology, and decreased cell viability and myelination potential. In vivo diffusion tensor imaging of the brain of CSPG4A131T mutation carriers demonstrated reduced white matter integrity compared to unaffected siblings and matched general population controls.
2021-09-23 10:14:20
dCTP (100 mM),用于高灵敏度和高重复性的PCR和RT-PCR,完整的单组分选择,可配置不同浓度dNTPs,
Cosmo Bio抗体,Cosmo Bio,Anti Dysbindin (Dystrobrevin-Binding Protein 1) pAb (Rabbit, Affinity Purified),CAC-ACC-PA007
Application: WB, IF, IHC(p)
Clonality: Polyclonal
Host: Rabbit
Purification: Purified – Affinity
Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
Background
Neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease have been increasing rapidly and have become a serious social problem. In recent years, new causative genes have been discovered for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and other intractable neurological diseases opening new avenues for research on pathogenesis. It has been suggested that aggregation and accumulation of specific proteins cause neurotoxicity and the formation of lesions, but the onset and progression mechanisms are still unclear. Neuropathological diagnostic and experimental model biomarkers are needed for drug construction, drug discovery, and therapeutic development.
Dysbindin is a component of the BLOC-1 complex, a complex that is required for normal biogenesis of lysosome-related organelles (LRO), such as platelet dense granules and melanosomes. In concert with the AP-3 complex, the BLOC-1 complex is required to target membrane protein cargos into vesicles assembled at cell bodies for delivery into neurites and nerve terminals. The BLOC-1 complex, in association with SNARE proteins, is also proposed to be involved in neurite extension. It plays a role in synaptic vesicle trafficking and in neurotransmitter release. 3 isoforms produced by alternative splicing and alternative initiation have been described. Isoform 1 is mainly cytoplasmic, but shuttles between the cytoplasm and nucleus. It is exported out of the nucleus via its nuclear export sequence (NES). Its nuclear localization is required for regulation of the expression of genes, such as SYN1. It is detected in neuron cell bodies, axons and dendrites and is mainly located to the postsynaptic density. Isoform 2 also shuttles between the cytoplasm and nucleus and is mainly expressed in the dendritic spine. It is predominantly a synaptic vesicle isoform but also highly expressed in the nucleus. Isoform 3 is exclusively cytoplasmic and is predominantly found in the postsynaptic density (PSD) with little association with synaptic vesicles. Mutations in DTNBP1 gene have been linked to Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome 7 (HPS7) that is characterized by oculocutaneous albinism, bleeding due to platelet storage pool deficiency, and lysosomal storage defects. Defects in DTNBP1 are associated with susceptibility to schizophrenia.
Western Blotting (WB): 0.3 µg/ml
Immunofluorescence (IF): 1 µg/ml
Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin) (IHC (P)): 1 µg/ml
Dysbindin-1
| Package Size | 50 µg |
|---|---|
| Form | Liquid (0.1M NaPB, pH7.0, 20 mg/ml BSA, 0.1% Sodium Azide (NaN3) added) |
| Concentration | 1 mg/mL |
| Purity | Affinity Purified |
| Host | Rabbit Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | MBP-tagged full length recombinant human Dysbindin. |
| Specificity | Dysbindin-1 |
| Cross Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Subclass | IgG |
| Storage | Store below -20°C. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. |
References
1) Ito H, Morishita R, Shinoda T, Iwamoto I, Sudo K, Okamoto K, Nagata KI. (2010) Dysbindin-1, WAVE2 and Abi-1 form a complex that regulates dendritic spine formation. Mol Psychiatry 15:976-986.
2) Ito H, Morishita R, Nagata K. (2016) Schizophrenia susceptibility gene product dysbindin-1 regulates the homeostasis of cyclin D1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1862: 1383-1391.
Cosmo Bio抗体,Cosmo Bio,Anti Alpha Synuclein (Amino Acids 11-20) pAb (Rabbit, Antiserum),CAC-TIP-SN-P02
Application: IHC, WB, ELISA
Clonality: Polyclonal
Host: Rabbit
Purification: Serum
Reactivity: Human, Mouse
Neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease have been increasing rapidly and have become a serious social problem. In recent years, new causative genes have been discovered for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and other intractable neurological diseases opening new avenues for research on pathogenesis. It has been suggested that aggregation and accumulation of specific proteins cause neurotoxicity and the formation of lesions, but the onset and progression mechanisms are still unclear. Neuropathological diagnostic and experimental model biomarkers are needed for drug construction, drug discovery, and therapeutic development.
Alpha-Synuclein, a 140-amino acid protein abundantly expressed in presynaptic terminals, is a component of intraneuronal or glial inclusions observed in cases of Parkinson’s disease (PD), Dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) and Multiple system atrophy (MSA). Although alpha-synuclein is a natively unfolded protein, fibrillization or conformational change(s) of alpha-synuclein is central to the pathogenesis of alpha-synucleinopathies. The amino-terminal region of alpha-synuclein consists of seven imperfect repeats, each 11 amino acids in length, with the consensus sequence KTKEGV. The repeats partially overlap with a hydrophobic region (amino acids 61-95). The carboxy-terminal region (amino acids 96-140) is negatively charged. These antibodies are powerful tools for biochemical and IHC analyses of neurodegenerative diseases and for evaluation of conformational changes of alpha-synuclein.
References:
1) Masami Masuda et al., Inhibition of a-synuclein fibril assembly by small molecules: Analysis using epitope-specific antibodies. FEBS Letters (2009) 583, 787-791. PMID 19183551
2) Motokuni Yonetani et al., Conversion of wild-type alpha-synuclein into mutant-type fibrils and its propagation in the presence of A30P mutant. Journal of Biological Chemistry (2009) 284, 7940-7950. PMID 19164293
Cosmo Bio抗体,Cosmo Bio,Anti Dewar Photoproducts (DewarPPs) mAb (Clone DEM-1),CAC-NM-DND-003
Application: ICC, ELISA, WB, IHC, FC, IP
Clonality: Monoclonal
Host: Mouse
Purification: Ammonium Sulfate
Reactivity: All
Prolonged exposure to solar UV radiation may result in harmful acute and chronic effects to the skin (including skin cancers), eye, and immune system. These harmful effects appear to be closely related to UV-induced DNA damage. Indeed, UV-induced DNA damage plays significant roles in cell-cycle arrest, activation of DNA repair, cell killing, mutation, and neoplastic transformation. The major types of DNA damage induced by solar UV radiation are cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPDs), (6–4) photoproducts (6-4PPs), and Dewar valence isomers of 6-4PPs (Dewar photoproducts; DewarPPs) formed between adjacent pyrimidine nucleotides on the same DNA strand. Approximately 70-80% of UV-induced DNA damage is CPDs and the remaining is 6-4PPs and Dewar isomers of 6-4PPs. DewarPPs are produced by the photoisomerization of 6-4PPs by UV radiation around 325 nm. In normal human cells these types of DNA lesions are repaired by nucleotide excision repair (NER).
To better study molecular events surrounding UV-induced DNA damage and repair, Matsunaga et. al. have established and characterized monoclonal antibodies against DewarPPs (9). These antibodies enable quantitation of DNA photoproducts from cultured cells or from skin epidermis using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). They also permit indirect immunofluorescence (IIF) visualization of DNA photoproducts in skin. This technology will contribute to understanding of molecular mechanisms of cellular responses to UV and DNA damage in many research fields including cancer research, photobiology, dermatology, ophthalmology, immunology, and cosmetology.
REACTIVITY:
1) DewarPPs in single-stranded DNA.
2) DewarPPs formed in TC, TT and CC dipyrimidine sequences.
3) DewarPPs formed in oligonucleotides consisting of more than eight bases.
References:
1) Douki, T. and Cadet. J, Biochemistry 40, 2495-2501 (2001).
2) Douki, T., et al., J. Biol. Chem., 275, 11678-11685 (2000).
3) Lee, J.H., et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 97, 4591-4596 (2000).
4) Perdiz, D., et al., J. Biol. Chem. 275, 26732-26742 (2000).
5) Kobayashi, N., et al., J. Biochem. 123, 182-188 (1998).
6) Clingen, P.H., et al., Photochem. Photobiol. 61, 163-170 (1995).
7) Clingen, P.H., et al., Cancer Res. 55, 2245-2248 (1995).
8) Chadwick, C.A., et al., J. Photochem. Photobiol. B. 28, 163-170 (1995).
9) Matsunaga, T., et al., Photochem. Photobiol. 57, 934-940 (1993).
10) Matsunaga, T., et al., Photochem. Photobiol. 54, 403-410 (1991).
11) Mitchell D.L. Mutat. Res., 194, 227-237 (1988).
Cosmo Bio抗体,Cosmo Bio,Anti Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 6 (PACE4) – Propeptide pAb (Rabbit, Antiserum),CAC-SK-T01-002
Application: WB, IHC, IP, ELISA
Clonality: Polyclonal
Host: Rabbit
Purification: Serum
Reactivity: Human
PACE4A is a member of the mammalian subtilisin-like proprotein convertase family which is responsible for the proteolytic activation of precursors into their biologically active forms. Previously we reported that the maturation of proPACE4A occurs via a intramolecular autoactivation and cleavage of the propeptide is a rate-limiting step for the secretion of PACE4A (Nagahama et al., FEBS Lett. (1998) 434, 155–159). Although PACE4A is a putative secretory enzyme, it matures and is secreted much slower than general secretory proteins. In this study, we investigated the molecular mechanism underlying this slow maturation. The deletion of 25 amino acids at the carboxy terminus is sufficient for a marked acceleration in both the maturation and secretion of PACE4A. The carboxyl-truncated proPACE4A existed only as a monomer-sized form in the endoplasmic reticulum, whereas the wild type of proPACE4A existed in larger forms. Further, the fusion construct of yellow fluorescent protein and the carboxy-terminal sequence of PACE4A associated with the proPACE4A moiety and inhibited maturation. Thus, the carboxy terminus of PACE4A functions as a potent autoinhibitor of its activation, resulting in the retention of proPACE4A in the endoplasmic reticulum. These findings indicate that PACE4A activity is highly controlled by a unique system at post-translational level. [from: Taniguchi T., Kuroda R., Sakurai K., Nagahama M., Wada I., Tsuji A., Matsuda Y. A Critical Role for the Carboxy Terminal Region of the Proprotein Convertase, PACE4A, in the Regulation of Its Autocatalytic Activation Coupled with Secretion (2002) Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 290(2) 878-884.]
Source: Professor Akihiko Tsuji, Faculty of Engineering, Tokushima University
2021-05-21 13:37:14
One Step Mouse Genotyping Kit,动物组织直接进行 PCR 反应的试剂盒,广泛适用于2 kb以内目标片段扩增,并适用于4对引物以内的多重PCR 反应。,
Cosmo Bio抗体,Cosmo Bio,Anti CD9 Antigen (MRP-1/Tspan-29) mAb (Clone 12A12, Biotin Labeled),CAC-SHI-EXO-M01-B
Application: ELISA, IP, WB
Clonality: Monoclonal
Conjugation: Biotin
Host: Mouse
Purification: Ig-PG
Reactivity: Human
Click here for more information and to see all exosome related products from Cosmo Bio USA.
CD9 is a cell surface glycoprotein which belongs to the tetraspanin superfamily. CD9 is known to complex with integrins and other transmembrane 4 superfamily proteins. It can modulate cell adhesion and migration and also trigger platelet activation and aggregation. Importantly, it is found on the surface of exosomes.
Exosomes are cell-derived vesicles bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and exhibiting a diameter of 50 to 150 nm. They are secreted from cultured cells and are observed in body fluids such as saliva, blood, urine, amniotic fluid, malignant ascites. Recent studies indicate that exosomes contain various proteins and RNAs, suggesting a role in information transfer between cells.
This monoclonal antibody can be used to immunoprecipitate exosomes from serum and culture supernatants.
References:
1) Shigeyasu Tsuda et al., Scientific Reports volume 7, Article number: 12989 (2017)
2) N Nishida-Aoki et al., Mol Ther. 2017 Jan 4;25(1):181-191. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2016.10.009.
3) Matsuzaki K et al., Oncotarget. 2017 Apr 11; 8(15): 24668–24678. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14969
4) Kazutoshi Fujita et al., Sci Rep. 2017; 7: 42961. doi: 10.1038/srep42961
5) Yoshioka Y et al., Nat Commun. 2014 Apr 7;5:3591. doi: 10.1038/ncomms4591.
6) Saito S et al., Sci Rep. 2018 Mar 5;8(1):3997. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-22450-2.
7) Yagi Y et al., Neurosci Lett. 2017 Jan 1;636:48-57. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2016.10.042. Epub 2016 Oct 22.
8) Ueda K et al., Sci Rep. 2014 Aug 29;4:6232. doi: 10.1038/srep06232.
Cosmo Bio抗体,Cosmo Bio,Anti 20S Proteasome Subunit Alpha Type-4 mAb (Clone GC3β),CAC-SZU-PS-M02
Application: WB
Clonality: Monoclonal
Host: Mouse
Purification: Ig-PG
Reactivity: Plant, Fish, Rat, Human, Yeast, Frog
Regulating protein stability and turnover is a key task in the cell. Besides lysosomes, ubiquitin‐mediated proteasomal degradation comprises the major proteolytic pathway in eukaryotes. Proteins destined for degradation by the proteasome are conjugated by a ‘tag’, a ubiquitin chain to a lysine, through an extensively regulated enzymatic cascade. The ubiquitylated proteins are subsequently targeted for degradation by the 26S proteasome, the major proteolytic machinery for ubiquitylated proteins in the cell. Ubiquitylation can be considered as another covalent post‐translational modification and signal, comparable to acetylation, glycosylation, methylation, and phosphorylation. However, ubiquitylation has multiple roles in addition to targeting proteins for degradation. Depending on the number of ubiquitin moieties and the linkages made, ubiquitin also plays an important role in DNA repair, protein sorting and virus budding. Unregulated degradation of proteins, or abnormally stable proteins, interfere with several regulatory pathways, and the ubiquitin‐proteasome pathway is affected in a number of diseases, such as neurodegenerative diseases, cellular atrophies and malignancies. Therefore, dissecting the ubiquitin‐proteasome pathway and identifying proteins involved in conjunction with the signals required for specific degradation of certain substrates, would help in developing novel therapeutic approaches to treat diseases where the ubiquitin‐proteasome pathway is impaired. [from: Roos‐Mattjus P. and Sistonen L. The ubiquitin‐proteasome pathway (2009) Annals of Medicine 36(4): 285-295]
The 26S proteasome is an essential component of the ubiquitin-proteolytic pathway in eukaryotic cells and is responsible for the degradation of most cellular proteins. It is composed of a 20S proteasome catalytic core and regulatory particles at either end. The subunits of the 20S proteasome are classified into two families, α and β. In eukaryotes, the 20S proteasome contains seven α-type subunits and seven β-type subunits. The fourteen subunits are arranged in four rings of seven and form an α7β7β7α7 structure. This antibody recognizes the α4 subunit of the 20S proteasome from all organisms tested from yeast to human.
References:
1) Tokumoto, M., Horiguchi, R., Nagahama, Y., Tokumoto, T. 1999. Identification of the Xenopus 20S proteasome alpha4 subunit which is modified in the meiotic cell cycle. Gene 239, 301-308. PubMed: 10548731
2) Tokumoto, M., Horiguchi, R., Nagahama, Y., Ishikawa, K., Tokumoto, T. 2000. Two proteins, a goldfish 20S proteasome subunit and the protein interacting with 26S proteasome, change in the meiotic cell cycle. Eur J Biochem 267, 97-103. PubMed: 10601855
Cosmo Bio抗体,Cosmo Bio,Anti Serpin B3 (SCCA1/T4-A) mAb (Clone SS6C),CAC-SU-IZ-M08
Application: IP, ELISA
Clonality: Monoclonal
Host: Rat
Purification: Ig-PG
Reactivity: Human
Squamous cell carcinoma antigen (SCCA) is a member of the ovalbumin family of serine proteinase inhibitors. The protein was isolated from a metastatic cervical squamous cell carcinoma by Kato and Torigoe (1977). SCCA is detected in the superficial and intermediate layers of normal squamous epithelium, whereas the mRNA is detected in the basal and sub-basal levels. The clinical import of SCCA has been as a circulating tumor marker for squamous cell carcinoma, especially those of the cervix, head and neck, lung, and esophagus. Many clinical studies of cervical squamous cell carcinoma show that the percentage of patients with elevated circulating levels of SCCA increases from approximately 12% at stage 0 to more than 90% at stage IV. Levels fall after tumor resection and rise in approximately 90% of the patients with recurrent disease. Similar trends occur in the other types of squamous cell carcinoma, with a maximum sensitivity of approximately 60% for lung, 50% for esophageal, and 55% for head and neck tumors. The neutral form of SCCA (SCCA1, or SERPINB3) is detected in the cytoplasm of normal and some malignant squamous cells, whereas the acidic form (SCCA2, or SERPINB4) is expressed primarily in malignant cells and is the major form found in the plasma of cancer patients. Thus, the appearance of the acidic fraction of SCCA is correlated with more aggressive tumors (summary by Schneider et al., 1995). Gene expression microarray profiling analysis has identified squamous cell cancer antigen (SCCA) as an IL-13 inflammation-induced gene in tracheal epithelial cells and keratinocytes. SCCA expression is increased in asthmatic bronchiale and atopic dermatitis skin. Two isoforms of SCCA are known: SCCA1 and SCCA2.
Source: Professor Kenji Dehara, Professor of Molecular Life Science, Faculty of Medicine, Saga University.
References:
1) The usefulness of combined measurements of squamous cell carcinoma antigens 1 and 2 in diagnosing atopic dermatitis. Shoichiro Ohta, et al. 2012. Ann Clin Biochem. 49: 277-284.
2) Characterization of novel squamous cell carcinoma antigen-related molecules in mice. Y. Sakata, et al. 2004. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 324(4):1340-1345.
3) The squamous cell carcinoma antigens as relevant biomarkers of atopic dermatitis. K. Mitsuishi, et al. 2005. Clin Exp Allergy 35:1327-1333.
4) Involvement of IL-32 in activation-induced cell death in T cells. Chiho Goda, et al. 2006. Int Immunol 18(2):233-240.
Cosmo Bio抗体,Cosmo Bio,Anti C9ORF72 (Poly-GA) pAb (Rabbit, Antiserum),CAC-TIP-C9-P01
Anti-C9ORF72 (Poly-GA) pAb — prepared from rabbits immunized with poly (GA)8 — recognizes poly (GA) dipeptide repeat proteins. Validated for ELISA and IHC(p), this antibody is useful for immunohistochemical and biochemical studies of C9ORF72 (Poly-GA) dipeptide species in diseased brains.
In 2011 hexanucleotide expansions in the C9ORF72 gene were identified in patients with frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). GGGGCC expansions are characterized pathologically by the presence of TDP-43 negative and p62 positive inclusions in granule cells of the cerebellum and in cells of the dentate gyrus and CA4 area of the hippocampus. It was reported that these inclusions included dipeptide repeat proteins, poly-GA, poly-GR and poly-GP, arising from a putative non-ATG initiated sense translation of the GGGGCC expansion. These antibodies are powerful tools for IHC analysis of neurodegenerative diseases.
Specifications
Recommended dilutions
References
2021-04-09 17:02:29
2 × Taq Plus Master Mix (Dye Plus),比普通,提高扩增产量和长度,
| 规格 | 价格 | 操作 |
|---|---|---|
| 186003534一支装,176001125三支装 | ¥7,799.00 | 询底价 |
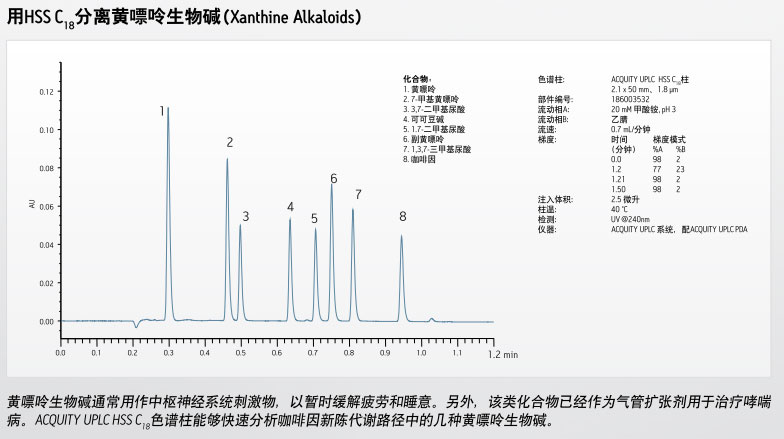
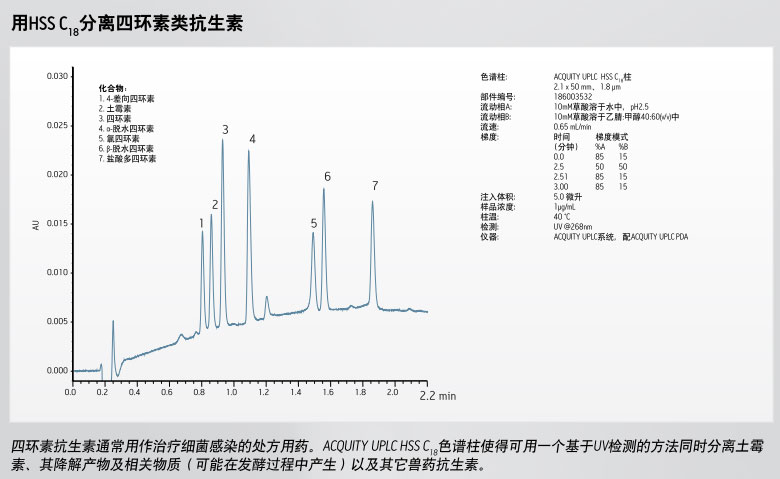
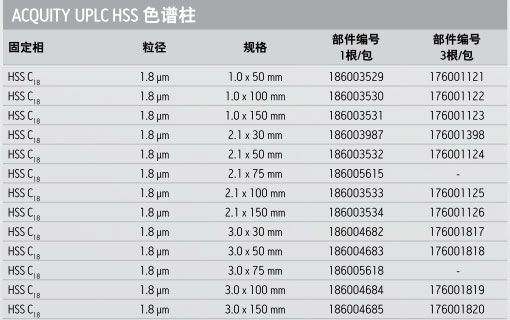
产品编号 : 186003534
具有高孔容的HPLC颗粒不具有足够的机械稳定性来承受UPLC分离技术所需要的高压、这一局限导致沃特世材料科学家研发出新的硅胶颗粒技术,专为提高机械强度以及具备合适的形态,以耐受高压条件而具有好的柱寿命和UPLC效率。于是,1.8μm HSS颗粒,是第一个也是仅有的100%硅胶颗粒,专门设计、测试以供UPLC应用,耐压高达18,000psig(1241 bar)。
HSS颗粒技术也具有HPLC粒径产品(2.5, 3.5和5 μm),对应于XSelect HSS HPLC柱家族,这确保在HPLC和UPLC技术平台之间方法可无缝转移。
耐压UPLC颗粒的设计与测试
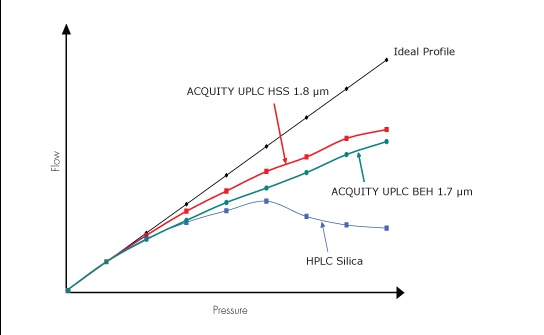
在此项沃特世特有的颗粒强度测试中,色谱颗粒被填充在柱中并施加流动相流速。随着压力的增加,颗粒会被碾碎,因而限制了流速。与理想剖面线的偏离程度表示了易碎性/强度。沃特世的BEH和HSS颗粒是目前市面上强度最好的多孔颗粒色谱填料。
ACQUITY UPLC HSS C18色谱柱
ACQUITY UPLC HSS C18的固定相特有三键键合C18基质和沃特世专有的端基封尾技术,不仅在中等pH流动相条件下对碱性化合物分析有很好的峰形,而且能够有效抑制酸性条件下的水解,从而延长了低pH值条件下的柱寿命。由于HSS颗粒是100%的超纯硅胶,ACQUITY UPLC HSS C18色谱柱能够在苛刻的强酸性条件下使用且具有优异性能。
由于pH值是方法开发中调控可离子化的化合物色谱分离选择性的重要参数,色谱柱在低pH条件下(如pH<2)的性能稳定性至关重要。ACQUITY UPLC HSS C18色谱柱是迄今为止市场上最稳定的键合相色谱柱系列,不会遭受以往依赖位阻保护技术(缺少封端)实现低pH稳定性色谱柱的常见峰形问题困扰。
ACQUITY UPLC HSS C18色谱柱在低pH值条件下能抑制酸性水解
低pH值稳定性:0.5% TFA,60°C条件下暴露21小时
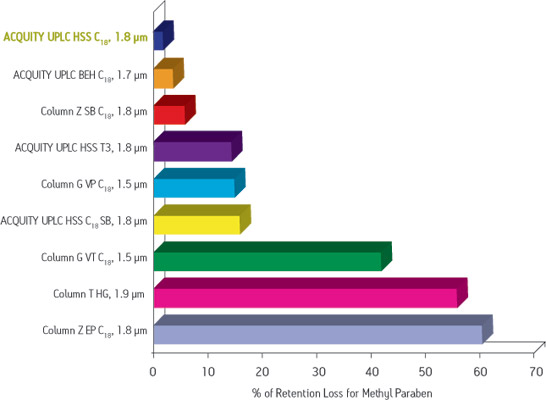
该组实验中,以中性标记物对羟基苯甲酸甲酯的保留丢失来表征酸性水解造成的键合相流失程度。ACQUITY UPLC HSS C18色谱柱采用了新型的键合和端基封尾技术,因此能够抑制键合相的流失。
注意:本页面内容仅供参考,所有资料请以沃特世官方网站(www.waters.com)为准。
ACQUITY UPLC HSS C18 1.8 µm, 2.1 x 150 mm信息由沃特世科技(上海)有限公司(Waters)为您提供,如您想了解更多关于ACQUITY UPLC HSS C18 1.8 µm, 2.1 x 150 mm报价、型号、参数等信息,欢迎来电或留言咨询。
注:该产品未在中华人民共和国食品药品监督管理部门申请医疗器械注册和备案,不可用于临床诊断或治疗等相关用途
2022-08-19 16:36:06
2 × Vazyme LAmp® Master Mix (Dye Plus),长距离PCR 的明灯,广泛的GC 适应性,图1.高扩增性能
2021-04-09 16:52:56
Taq DNA Polymerase (Mg2+ free Buffer),高纯度耐热DNA聚合酶,
Cosmo Bio抗体,Cosmo Bio,Anti Canine T-Cell Surface Glycoprotein CD3 Epsilon Chain (CD3E) mAb (Clone 1B9-7-1-1),CAC-ABS-070001
Application: WB
Clonality: Monoclonal
Host: Mouse
Purification: Ig-PG
Reactivity: Dog
Background
The CD3-epsilon polypeptide, which together with CD3-gamma, -delta and -zeta, and the T-cell receptor alpha/beta and gamma/delta heterodimers, forms the T cell receptor-CD3 complex. This complex plays an important role in coupling antigen recognition to several intracellular signal-transduction pathways. The genes encoding the epsilon, gamma and delta polypeptides are located in the same cluster on chromosome 11. The epsilon polypeptide plays an essential role in T-cell development.[7] [from: Wikipedia contributors. (2018, October 25). T-cell surface glycoprotein CD3 epsilon chain. In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved 21:31, June 3, 2019]
| Intended use | Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user. Not tested by IHC. |
| Antigen/Source | CD3ε |
| Host | Mouse |
| Immunogen | Canine |
| Reacts with | Canine |
| Not Reacts with | Feline |
| Clone | 1B9-7-1-1 |
| Isotype | IgG1 |
| Fraction | Affinity Purified |
| Applications | Western Blot |
| Preservative | 0.09% NaN3 in LIQ |
| Other | [Cross reactivity] Canine (Do not react with feline) |
| Storage | 4C DNF |
Cosmo Bio抗体,Cosmo Bio,Anti Monocarboxylate transporter 2 (MCT2) pAb (Rabbit, Antiserum),CAC-YCU-M-MCT2A
Application: WB
Clonality: Polyclonal
Host: Rabbit
Purification: Serum
Reactivity: Mouse
A transport protein (variously referred to as a transmembrane pump, transporter, escort protein, acid transport protein, cation transport protein, or anion transport protein) is a protein that serves the function of moving other materials within an organism. Transport proteins are vital to the growth and life of all living things. There are several different kinds of transport proteins. Carrier proteins are proteins involved in the movement of ions, small molecules, or macromolecules, such as another protein, across a biological membrane.[1] Carrier proteins are integral membrane proteins; that is, they exist within and span the membrane across which they transport substances. The proteins may assist in the movement of substances by facilitated diffusion (i.e., passive transport) or active transport. These mechanisms of movement are known as carrier-mediated transport.[2] Each carrier protein is designed to recognize only one substance or one group of very similar substances. Research has correlated defects in specific carrier proteins with specific diseases.[3] A membrane transport protein (or simply transporter) is a membrane protein[4] that acts as such a carrier. [from: Wikipedia contributors. (2019, May 9). Transport protein. In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved 18:43, June 6, 2019, from https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Transport_protein&oldid=896329420]
MCT2 is a proton-coupled monocarboxylate transporter is encoded in humans by the SLC16A7 gene.[5] It catalyzes the rapid transport across the plasma membrane of many monocarboxylates such as lactate, branched-chain oxo acids derived from leucine, valine and isoleucine, and the ketone bodies acetoacetate and beta-hydroxybutyrate. It also functions as high-affinity pyruvate transporter. Both Northern blot analysis and inspection of the human expressed sequence tag (EST) database suggest relatively little expression of MCT2 in human tissues. As well, the sequence of MCT2 is far less conserved across species than that of MCT1 or MCT4 and there also appear to be considerable species differences in the tissue expression profile of this isoform. Of the four known mammalian lactate transporters (MCTs 1-4), MCT2 harbors the highest affinity for lactate.[6] In parallel, MCT2 gene transcription has been demonstrated to respond with high-sensitivity to hypoxia, intracellular pH, and, to lactate.[7] [from: Wikipedia contributors. (2019, April 20). Monocarboxylate transporter 2. In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved 18:41, June 6, 2019, from https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Monocarboxylate_transporter_2&oldid=893305296]
References:
1) Watanabe-Kaneko K, et al. (2007) The synaptic scaffolding protein Delphilin interacts with monocarboxylate transporter 2. Neuroreport. 18(5):489-493.
Cosmo Bio抗体,Cosmo Bio,Anti DEP Domain-Containing Protein 1B (XTP1/XTP8) mAb (Clone 2191H11),CAC-PRPG-XTP-M01
Application: WB, IHC
Clonality: Monoclonal
Host: Mouse
Purification: Supernatant
Reactivity: Human
The RhoGAP family embraces a unique member named XTP1 (also referred to as DEPDC1B, BRCC3 or FLJ11252) and pairing with a homologue denoted SDP35 (also referred to as DEPDC1, DEP8, FLJ20354 or DEPDC1-V2). The structural-functional properties of XTP1 are still largely unknown, but its structural uniqueness resides in the presence of a domain showing homology with Dishwelled, i.e. the DEP domain (Dishwelled/Pleckstrin-like domain). The presence of this domain suggests that XTP1 might engage in more complex molecular interactions than those of other members of the family. Another peculiar feature of XTP1 is represented by its atypical GAP domain, which lacks the orthodox “Arg finger” catalytic motif essential for exerting canonical GAP function. Whereas most RhoGAP family members are either ubiquitously expressed throughout the body or are concentrated in discrete tissue/organs, XTP1 is remarkably poorly represented in most human adult tissues (also supported by evidence provided by the Comparative Cancer Genome Project database). XTP1 is de novo expressed upon neoplastic transformation and remains abundant in many cancer cell lines. Some observations in epithelial tumors suggest that it may act as a cell-cycle regulator.
Catalog numbers beginning with “CAC” are antibodies from our exclusive Cosmo Bio Antibody Collection. Visit the CAC Antibody homepage to browse the collection list, organized by research topic.
Click here to browse a well organized list of products for Bone, Collagen, and Extracellular Matrix research.
Please click here to view other Bone-related Products
Application: WB, IP, IHC
Clonality: Monoclonal
Host: Mouse
Purification: Purified – Affinity
Reactivity: Bovine, Mouse, Rat, Human
Lect1 encodes a glycosylated transmembrane protein that is cleaved to form a mature, secreted protein. The N-terminus of the precursor protein shares characteristics with other surfactant proteins and is sometimes called chondrosurfactant protein, although no biological activity has yet been defined for it. The C-terminus of the precursor protein contains a 25 kDa mature protein called leukocyte cell-derived chemotaxin-1 or chondromodulin-1. The mature protein promotes chondrocyte growth and inhibits angiogenesis. This gene is expressed in the avascular zone of prehypertrophic cartilage, and its expression decreases during chondrocyte hypertrophy and vascular invasion. The mature protein likely plays a role in endochondral bone development by permitting cartilaginous anlagen to be vascularized and replaced by bone. It may also be involved in the broad control of tissue vascularization during development. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms.[7] [from: Wikipedia contributors. (2017, October 27). LECT1. In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved 17:42, June 3, 2019, from https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=LECT1&oldid=807301938]
Cosmo Bio抗体,Cosmo Bio,Anti Human Transmembrane Glycoprotein NMB (GPNMB) pAb (Rabbit, Purified Ig),CAC-ICA-TG1-RBP1
Application: FC, ELISA, IHC
Clonality: Polyclonal
Host: Rabbit
Purification: Ig-PA
Reactivity: Human
Lipid-laden macrophages may orchestrate pathology, an accepted notion for inborn lysosomal storage disorders (LSDs) and more recently for metabolic syndrome. The development of enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) for specific LSDs has led in the last decades to the identification of markers of lipid-laden macrophages. In LSDs characterized by foamy macrophages as storage cells, plasma GPNMB has been shown to accurately reflect disease burden. Moreover, GPNMB is also applicable in mouse models of LSDs like Gaucher disease and Niemann-Pick type C. GPNMB is also increased in several acquired diseases, such as metabolic syndrome and neurodegeneration. It therefore might be that these disease conditions share pathophysiological elements, in particular the accumulation of foamy, lysosomal stressed, macrophages. GPNMB is among the most upregulated proteins in lipid-laden macrophages. Nevertheless, at present its exact function in foamy macrophage remains largely enigmatic. Important unanswered questions concern the function(s) served by GPNMB, either the cellular membrane-bound or (extracellular) soluble isoforms, in lipid-laden macrophages and beyond. GPNMB is also expressed in melanocytes. GPNMB has been suggested to be involved in the delay of cell growth and regulation of metastasis. In recent years, Professor Hideaki Hara’s group at Gifu Pharmaceutical University, and others have shown that GPNMB expression is suppressed in mice that have developed amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), and tracking of GPNMB dynamics and function has been shown to be useful for ALS research.
Cosmo Bio抗体,Cosmo Bio,Anti Feline T-Cell Surface Glycoprotein CD3 Epsilon Chain (CD3E) mAb (Clone 5G-6-7-3),CAC-ABS-070002
Application: FC, ELISA, WB
Clonality: Monoclonal
Host: Mouse
Purification: Ig-PG
Reactivity: Cat
Background
The CD3-epsilon polypeptide, which together with CD3-gamma, -delta and -zeta, and the T-cell receptor alpha/beta and gamma/delta heterodimers, forms the T cell receptor-CD3 complex. This complex plays an important role in coupling antigen recognition to several intracellular signal-transduction pathways. The genes encoding the epsilon, gamma and delta polypeptides are located in the same cluster on chromosome 11. The epsilon polypeptide plays an essential role in T-cell development.[7] [from: Wikipedia contributors. (2018, October 25). T-cell surface glycoprotein CD3 epsilon chain. In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved 21:31, June 3, 2019]
| Antigen/Source | CD3ε |
| Host | Mouse |
| Immunogen | Feline |
| Reacts with | Feline |
| Not Reacts with | Canine |
| Clone | 5G-6-7-3 |
| Isotype | IgG1 |
| Fraction | Affinity Purified |
| Applications | Western Blot/Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay/Flow Cytometry |
| Storage | 4C |
Catalog numbers beginning with “CAC” are antibodies from our exclusive Cosmo Bio Antibody Collection. Visit the CAC Antibody homepage to browse the collection list, organized by research topic.
Click here to browse a well organized list of products for Bone, Collagen, and Extracellular Matrix research.
Please click here to view other Bone-related Products
Application: WB, IP, IHC
Clonality: Monoclonal
Host: Mouse
Purification: Purified – Affinity
Reactivity: Bovine, Mouse, Rat, Human
Lect1 encodes a glycosylated transmembrane protein that is cleaved to form a mature, secreted protein. The N-terminus of the precursor protein shares characteristics with other surfactant proteins and is sometimes called chondrosurfactant protein, although no biological activity has yet been defined for it. The C-terminus of the precursor protein contains a 25 kDa mature protein called leukocyte cell-derived chemotaxin-1 or chondromodulin-1. The mature protein promotes chondrocyte growth and inhibits angiogenesis. This gene is expressed in the avascular zone of prehypertrophic cartilage, and its expression decreases during chondrocyte hypertrophy and vascular invasion. The mature protein likely plays a role in endochondral bone development by permitting cartilaginous anlagen to be vascularized and replaced by bone. It may also be involved in the broad control of tissue vascularization during development. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms.[7] [from: Wikipedia contributors. (2017, October 27). LECT1. In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved 17:42, June 3, 2019, from https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=LECT1&oldid=807301938]
2021-12-24 10:56:47
本品为不含甘油的Taq HS DNA polymerase,可以用于冻干。Taq HS DNA polymerase是由Champagne Taq antibody与Taq DNA polymerase经过一定比例混合得到的热启动Taq酶。基于Champagne Taq antibody的热稳定特性,Taq HS DNA polymerase在55℃下仍可保持严格的封闭性,使得混样和体系升温阶段非特异扩增被抑制到较低程度。当反应在95℃保持30 sec以上时,Champagne Taq antibody彻底失活,Taq酶活性被完全释放,保证了PCR体系具有较高的扩增灵敏度和特异性。Taq HS DNA polymerase的激活不受缓冲液pH、离子强度等因素的影响,适用于各种基于Taq DNA polymerase的热启动PCR、qPCR反应,常用于从复杂模板(基因组,cDNA)中扩增低拷贝基因,是基于PCR/qPCR分子诊断试剂的热启动Taq酶。
95℃加热 30 s 即可完全释放 Taq 酶活性
较高的扩增灵敏度和特异性
对各种 PCR/qPCR 体系具有兼容性
-30 ~ -15℃保存,≤0℃运输。
2021-09-13 14:46:29
dNTP Mix ( 2.5 mM each) ,用于高灵敏度和高重复性的PCR和RT-PCR,
Cosmo Bio抗体,Cosmo Bio,Anti Androstenedione pAb (Rabbit, Antiserum),CAC-KZ-HS-P15
Application: ELISA, RIA
Clonality: Polyclonal
Host: Rabbit
Purification: Serum
Reactivity: Bovine, Human, Rat, Mouse, Chicken
Androstenedione, or 4-androstenedione (abbreviated as A4 or Δ4-dione), also known as androst-4-ene-3,17-dione, is an endogenous weak androgen steroid hormone and intermediate in the biosynthesis of estrone and of testosterone from dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA). It is closely related to androstenediol (androst-5-ene-3β,17β-diol). Androstenedione is a precursor of testosterone and other androgens, as well as of estrogens like estrone, in the body. In addition to functioning as an endogenous prohormone, androstenedione also has weak androgenic activity in its own right. Androstenedione has been found to possess some estrogenic activity, similarly to other DHEA metabolites.[2] However, in contrast to androstenediol, its affinity for the estrogen receptors is very low, with less than 0.01% of the affinity of estradiol for both the ERα and ERβ.[3] [from: Wikipedia contributors. (2019, April 7). Androstenedione. In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved 20:45, June 3, 2019, from https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Androstenedione&oldid=891404493]
Cosmo Bio抗体,Cosmo Bio,Anti Alpha Synuclein (Amino Acids 61-70) pAb (Rabbit, Antiserum),CAC-TIP-SN-P07
Application: IHC, WB, ELISA
Clonality: Polyclonal
Host: Rabbit
Purification: Serum
Reactivity: Human, Mouse
Neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease have been increasing rapidly and have become a serious social problem. In recent years, new causative genes have been discovered for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and other intractable neurological diseases opening new avenues for research on pathogenesis. It has been suggested that aggregation and accumulation of specific proteins cause neurotoxicity and the formation of lesions, but the onset and progression mechanisms are still unclear. Neuropathological diagnostic and experimental model biomarkers are needed for drug construction, drug discovery, and therapeutic development.
Alpha-Synuclein, a 140-amino acid protein abundantly expressed in presynaptic terminals, is a component of intraneuronal or glial inclusions observed in cases of Parkinson’s disease (PD), Dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) and Multiple system atrophy (MSA). Although alpha-synuclein is a natively unfolded protein, fibrillization or conformational change(s) of alpha-synuclein is central to the pathogenesis of alpha-synucleinopathies. The amino-terminal region of alpha-synuclein consists of seven imperfect repeats, each 11 amino acids in length, with the consensus sequence KTKEGV. The repeats partially overlap with a hydrophobic region (amino acids 61-95). The carboxy-terminal region (amino acids 96-140) is negatively charged. These antibodies are powerful tools for biochemical and IHC analyses of neurodegenerative diseases and for evaluation of conformational changes of alpha-synuclein.
References:
1) Masami Masuda et al., Inhibition of a-synuclein fibril assembly by small molecules: Analysis using epitope-specific antibodies. FEBS Letters (2009) 583, 787-791. PMID 19183551
2) Motokuni Yonetani et al., Conversion of wild-type alpha-synuclein into mutant-type fibrils and its propagation in the presence of A30P mutant. Journal of Biological Chemistry (2009) 284, 7940-7950. PMID 19164293
2021-01-14 15:06:12
Green Taq Mix,优化的缓冲体系,有效抑制非特异性扩增,
Cosmo Bio抗体,Cosmo Bio,Anti Ginsenoside Rb1 mAb (Clone 9G7),CAC-KYU-HT-M003
Application: ELISA, WB
Clonality: Monoclonal
Host: Mouse
Purification: Ig-PG
Within the fields of molecular biology and pharmacology, a small molecule is a low molecular weight (< 900 daltons) organic compound that may regulate a biological process, with a size on the order of 1 nm. Most drugs are small molecules. Larger structures such as nucleic acids and proteins, and many polysaccharides are not small molecules, although their constituent monomers (ribo- or deoxyribonucleotides, amino acids, and monosaccharides, respectively) are often considered small molecules. Small molecules may be used as research tools to probe biological function as well as leads in the development of new therapeutic agents. Some can inhibit a specific function of a protein or disrupt protein–protein interactions.
Pharmacology usually restricts the term “small molecule” to molecules that bind specific biological macromolecules and act as an effector, altering the activity or function of the target. Small molecules can have a variety of biological functions or applications, serving as cell signaling molecules, drugs in medicine, pesticides in farming, and in many other roles. These compounds can be natural (such as secondary metabolites) or artificial (such as antiviral drugs); they may have a beneficial effect against a disease (such as drugs) or may be detrimental (such as teratogens and carcinogens). [from: Wikipedia contributors. (2019, April 6). Small molecule. In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved 19:49, May 29, 2019, from https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Small_molecule&oldid=891243496]
Ginsenoside Rb1 is a saponin isolated from Panax ginseng.
References:
1) Tanaka H. et al., Formation of monoclonal antibody against a major ginseng component, ginsenoside Rb1 and its characterization, Cytotechnology, 29,115, 1999. PMID:22359060.
2) Fukuda N, Tanaka H, Shoyama Y. (2001) Double staining of ginsenosides by Western blotting using anti-ginsenoside Rb1 and Rg1 monoclonal antibodies. Biol Pharm Bull. 24(10):1157-60. PMID:11642323.
2021-04-09 16:57:53
2 × Taq Master Mix for PAGE,产物适合于聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳的DNA聚合酶,
Cosmo Bio抗体,Cosmo Bio,Anti-Latency-Associated Peptide (LAP) Plasma Kallikrein Degradation Fragment R58 mAb (Clone 18F9-16),CAC-RIK-MA-R58
Background
Anti-Latency-Associated Peptide (LAP) Plasma Kallikrein Degradation Fragment R58-specific mAb 18F9-16 was cloned from mice immunized with R58 peptide [CGQILSKLR]. 18F9-16 recognizes the C-terminus cut end of LAP degradation product (LAP-D) R58 produced when latent TGF-β is digested with Plasma Kallikrein. 18F9-16 is validated for IHC and IF.
TGF-β is produced as a pro-protein latent complex in which a 25 kDa active TGF-β fragment is trapped by an N-terminal pro-peptide called Latency Associated Protein (LAP). Active TGF-β is released from the latent complex in a process called the TGF-β activation reaction involving a conformational change induced by binding of the latent complex to cell adhesion proteins such as thrombospondin and integrins, and/or by being cleaved by serine proteases, cysteine proteases, and MMPs in an organ and context-depending manner.
Kojima and his colleagues in the Cellular Molecular Pathology Research Unit (currently, Center for Integrative Medical Sciences, Liver Cancer Prevention Research Unit), RIKEN, Japan focused on the role of serine proteases plasmin and plasma kallikrein in the release and activation of TGF-β and its involvement in liver diseases. They showed that plasmin and plasma kallikrein cleave, respectively, at Lys56-Leu57 and Arg58-Leu59 within the LAP portion of the latent TGF-β1 molecule. The anti-TGF-β1 LAP-degradate (LAP-D) antibodies are useful for investigating the molecular mechanism of TGF-β activation and its related diseases, including liver fibrosis/cirrhosis and liver degeneration.
Applications
Specifications
| Package Size | 100 µg |
|---|---|
| Solution | Liquid, PBS (pH 7.4), 0.05% NaN3 |
| Concentration | 1 mg/mL |
| Purity | Purified from cell culture of serum-free medium by affinity column (Protein G) |
| Species | Monoclonal Mouse IgG1 clone # 6D6 |
| Immunogen | L59 peptide [LASPPSQGEVPGGC] |
| Specificity | Recognizes N-terminus cut end of LAP degradates (LAP-D) L59 when latent TGF-β is digested with Plasma Kallikrein (PLK). |
| Storage | Store below -20°C. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. |
References
Cosmo Bio抗体,Cosmo Bio,Anti CD63 Antigen (LAMP-3/Tspan-30) (Clone 8A12, TF2SW Labeled),CAC-SHI-EXO-M02-TF2
Application: FC
Clonality: Monoclonal
Conjugation: Tide Fluor™ 2SW
Host: Mouse
Purification: Ig-PG
Reactivity: Human
Click here for more information and to see all exosome related products from Cosmo Bio USA.
CD63 (also known as LAMP-3, Melanoma-associated antigen ME491, TSPAN30, MLA1 and OMA81H) is a cell surface glycoprotein which belongs to the tetraspanin superfamily. CD63 is known to complex with integrins. CD63 is expressed on activated platelets, monocytes and macrophages, and is weakly expressed on granulocytes, T cells and B cells. Importantly, it is found on the surface of exosomes.
Exosomes are cell-derived vesicles bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and exhibiting a diameter of 50 to 150 nm. They are secreted from cultured cells and are observed in body fluids such as saliva, blood, urine, amniotic fluid, malignant ascites. Recent studies indicate that exosomes contain various proteins and RNAs, suggesting a role in information transfer between cells.
This monoclonal antibody can be used to immunoprecipitate exosomes from serum and culture supernatants.
References:
1) Yoshioka Y et al., Nat Commun. 2014 Apr 7;5:3591. doi: 10.1038/ncomms4591.
2) N Nishida-Aoki et al., Mol Ther. 2017 Jan 4;25(1):181-191. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2016.10.009. 3) Saito S et al., Sci Rep. 2018 Mar 5;8(1):3997. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-22450-2.
产品介绍 产品介绍 相关方案 全部规格 全部规格 产品介绍 通常把粒径在10微米以下的颗粒物称为PM10,又称为可吸入颗粒物或飘尘。我公司根据《空气总悬浮颗粒物技术标准》所销售的PM10滤纸带,通过与国外同类产品进行对比,具有过滤精度高、数据准确的特点,达到了国际技术水平,现已应用到全国各地环境保护局环境监测站和国内外空气自动监测仪器厂家,得到了用户认可。 适用仪器型号:METONE公司 BAM1020 ,法国ESA ,美国赛默飞世尔,北京中晟泰科,武汉天虹,杭州大地等, 具体规格尺寸电询。 技术参数 规格:φ40×φ90×30mm(可定制) 中心轴孔径×纸带外径×纸带宽度允许盘径误差≤2.0mm 产品质量技术标准: 厚度0.24-3.0mm 强度≥1000g 阻力≤5.2mmH2O(气流比速为0.06升/分?厘米2) 效率≥99.9%(油雾法:对≥0.3μm的油雾粒子) 全部规格 MET ONE PM10 纸带 1个
Cosmo Bio抗体,Cosmo Bio,Anti CD81 Antigen (TAPA-1/Tspan-28) mAb (Clone 12C4),CAC-SHI-EXO-M03-50
Application: IP, WB
Clonality: Monoclonal
Host: Mouse
Purification: Ig-PG
Reactivity: Bovine, Human
Click here for more information and to see all exosome related products from Cosmo Bio USA.
CD81 (TAPA-1) is a cell surface protein which belongs to the tetraspanin superfamily. CD81 is identified as a component of the B lymphocyte receptor (BCR) and as a receptor for the Hepatitis C Virus. Importantly, it is found on the surface of exosomes.
Exosomes are cell-derived vesicles bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and exhibiting a diameter of 50 to 150 nm. They are secreted from cultured cells and are observed in body fluids such as saliva, blood, urine, amniotic fluid, malignant ascites. Recent studies indicate that exosomes contain various proteins and RNAs, suggesting a role in information transfer between cells.
This monoclonal antibody can be used to immunoprecipitate exosomes from serum and culture supernatants.
References:
1) Takahashi A et al., Nat Commun. 2017 May 16;8:15287. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15287.
2) M Somiya et al., J Extracell Vesicles. 2018 Feb 21;7(1):1440132. doi:10.1080/20013078.2018.1440132. eCollection 2018.
Cosmo Bio抗体,Cosmo Bio,Anti Human/Rat/Mouse Transmembrane Glycoprotein NMB (GPNMB) pAb (Rabbit, Purified Ig),CAC-ICA-TG1-RBP3
Application: FC, ELISA, IHC
Clonality: Polyclonal
Host: Rabbit
Purification: Ig-PA
Reactivity: Mouse, Rat, Human
Lipid-laden macrophages may orchestrate pathology, an accepted notion for inborn lysosomal storage disorders (LSDs) and more recently for metabolic syndrome. The development of enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) for specific LSDs has led in the last decades to the identification of markers of lipid-laden macrophages. In LSDs characterized by foamy macrophages as storage cells, plasma GPNMB has been shown to accurately reflect disease burden. Moreover, GPNMB is also applicable in mouse models of LSDs like Gaucher disease and Niemann-Pick type C. GPNMB is also increased in several acquired diseases, such as metabolic syndrome and neurodegeneration. It therefore might be that these disease conditions share pathophysiological elements, in particular the accumulation of foamy, lysosomal stressed, macrophages. GPNMB is among the most upregulated proteins in lipid-laden macrophages. Nevertheless, at present its exact function in foamy macrophage remains largely enigmatic. Important unanswered questions concern the function(s) served by GPNMB, either the cellular membrane-bound or (extracellular) soluble isoforms, in lipid-laden macrophages and beyond. GPNMB is also expressed in melanocytes. GPNMB has been suggested to be involved in the delay of cell growth and regulation of metastasis. In recent years, Professor Hideaki Hara’s group at Gifu Pharmaceutical University, and others have shown that GPNMB expression is suppressed in mice that have developed amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), and tracking of GPNMB dynamics and function has been shown to be useful for ALS research.
| 规格 | 操作 |
|---|---|
| 不同的吸附剂不同规格 | 询底价 |
Sep-Pak产品被全球认可,并保持作为GC/MS, HPLC和LC/MS分析的最标准的SPE产品,具有多种填料和配置以满足96孔板和拥有专利的uElution板的模式。每种配置提供特定的功能,但它们都包含同样高质量的反相、正相、离子交换和特殊应用的装填吸附剂。这使方法转换变得直接和可预测。
Sep-Pak96孔提取板
Sep-Pak 96孔提取板中填充的化学吸附剂与应用多年的Sep-Pak小柱相同。这些板已被用于高容量样品的处理,96孔板可在自动化样品处理系统中以及标准真空装置中应用。Sep-Pak提取板有各种不同填充质量的吸附剂以适合不同的上样量。
Sep-Pak96孔提取板都经过多方面的质量控制检测。每一块板都有一个分析证书,包括硅胶原料和硅胶键合相键合密度、洁净度和色谱选择性的性能报告。提取板经制造和测试确保96个孔流速恒定。
反相
C18
tC18
C8
tC2 –
Porapak? RDX
反相或正相
氨基丙基(NH2)
氰基丙基(CN)
Diol –
正相
硅胶
氧化铝 (A, B & N)
Florisil
离子交换
Accell? Plus QMA –
Accell? Plus CM –
注意:本页面内容仅供参考,所有资料请以沃特世官方网站(www.waters.com)为准。
Sep-Pak SPE固相提取小柱信息由沃特世科技(上海)有限公司(Waters)为您提供,如您想了解更多关于Sep-Pak SPE固相提取小柱报价、型号、参数等信息,欢迎来电或留言咨询。
注:该产品未在中华人民共和国食品药品监督管理部门申请医疗器械注册和备案,不可用于临床诊断或治疗等相关用途
2021-05-21 13:37:12
Heat-labile UDG,UDG (Uracil-DNA Glycosylase,尿嘧啶-DNA 糖基化酶)可催化水解含有dU 的DNA 单链或双链的尿嘧啶碱基和糖磷酸骨架的N- 糖苷键,释放游离尿嘧啶,由此产生的无碱基位点很容易被水解断裂。Heat-labile Uracil DNA Glycosylase 来源于嗜冷海洋细菌,对高温敏感,55℃ 10 min 就可以使酶不可逆失活。Heat-labile UDG在多种常见的PCR Buffer 中都有很高的活性,适用于PCR/qPCR、RT-PCR/RT-qPCR 体系。,
Catalog numbers beginning with “CAC” are antibodies from our exclusive Cosmo Bio Antibody Collection. Visit the CAC Antibody homepage to browse the collection list, organized by research topic.
Application: FC
Clonality: Monoclonal
Conjugation: Tide Fluor™ 2SW
Host: Mouse
Purification: Ig-PG
Reactivity: Human
Click here for more information and to see all exosome related products from Cosmo Bio USA.
CD9 is a cell surface glycoprotein which belongs to the tetraspanin superfamily. CD9 is known to complex with integrins and other transmembrane 4 superfamily proteins. It can modulate cell adhesion and migration and also trigger platelet activation and aggregation. Importantly, it is found on the surface of exosomes.
Exosomes are cell-derived vesicles bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and exhibiting a diameter of 50 to 150 nm. They are secreted from cultured cells and are observed in body fluids such as saliva, blood, urine, amniotic fluid, malignant ascites. Recent studies indicate that exosomes contain various proteins and RNAs, suggesting a role in information transfer between cells.
This monoclonal antibody can be used to immunoprecipitate exosomes from serum and culture supernatants.
References:
1) Shigeyasu Tsuda et al., Scientific Reports volume 7, Article number: 12989 (2017)
2) N Nishida-Aoki et al., Mol Ther. 2017 Jan 4;25(1):181-191. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2016.10.009.
3) Matsuzaki K et al., Oncotarget. 2017 Apr 11; 8(15): 24668–24678. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14969
4) Kazutoshi Fujita et al., Sci Rep. 2017; 7: 42961. doi: 10.1038/srep42961
5) Yoshioka Y et al., Nat Commun. 2014 Apr 7;5:3591. doi: 10.1038/ncomms4591.
6) Saito S et al., Sci Rep. 2018 Mar 5;8(1):3997. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-22450-2.
7) Yagi Y et al., Neurosci Lett. 2017 Jan 1;636:48-57. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2016.10.042. Epub 2016 Oct 22.
8) Ueda K et al., Sci Rep. 2014 Aug 29;4:6232. doi: 10.1038/srep06232.
Cosmo Bio抗体,Cosmo Bio,Anti TAR DNA-Binding Protein 43 (TDP43), phospho Ser410 pAb (Rabbit, Antiserum),CAC-TIP-PTD-P04
Anti-TAR DNA-Binding Protein 43 (TDP-43), phospho Ser410 pAb was prepared from rabbits immunized with phospho-peptide [CMDSKSS(p)GWGM]. This pAb recognizes human TDP-43 phosphorylated on serine 410 and is validated for western blot, ELISA and IHC(f) analyses of TDP-43 proteinopathy.
TDP-43, a heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein, was identified as a component of ubiquitin-positive and tau-negative inclusions observed in cases of frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD-U) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Immunochemical analyses using antibodies generated against phospho- and non-phosphopeptides of human TDP-43 revealed that abnormally phosphorylated full-length TDP-43 (45 kDa), C-terminal fragments (~25 kDa) and smearing substances are deposited as intracellular inclusions in affected regions of FTLD-U and ALS cases. This antibody is a powerful tool for biochemical and immunohistochemical analyses of neurodegenerative diseases and for evaluation of cellular or animal models of TDP-43 proteinopathy.
Specifications
Recommended dilutions
References
â¢Â
2022-05-27 09:48:21
2 × Phanta® Max Master Mix,模板兼容性强的新一代高保真DNA聚合酶,以人基因组为模板扩增 654 bp、 900 bp、 800 bp、 1,200 bp、 1,400 bp、426 bp 目标片段,各扩增子 GC 含量均高于 68%。
产品介绍 产品介绍 相关方案 全部规格 产品介绍 高温编织带WT-3×100是套管绝缘软线、软管、热电偶和感应线圈的理想热绝缘体、填充物、垫圈、液态金属防溅保护带、伸缩接头。 产品型号 高温编织带WT-3×100 主要特点 1、主要由石棉、陶瓷纤维编织而成,不支持胶带。 2、连续工作温度高达1500℃。 3、强度高,使用灵活、耐用,化学稳定性好,且具有优良的电阻性。 4、对皮肤无刺激,无毒,不会燃烧。 5、耐熔融金属火花飞溅及大多数化学药品和溶剂腐蚀。
| 规格 | 操作 |
|---|---|
| Atlantis T3 | 询底价 |
Atlantis T3高效液相色谱柱以及ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3色谱柱的卓越性能来自于沃特世公司先进的T3键合技术,它采用三官能团C18烷基键合相,保证键合密度能提升极性化合物的保留并且100%水相流动相兼容。并且,专有的端基封尾技术比传统的的TMS封尾方法能够将更多的游离硅羟基反应完全。因此,键合和端基封尾技术的完美结合保证Atlantis T3色谱柱的卓越性能。
T3的应用优势:
● 保留极性化合物首选
● 完美保留平衡一对不同极性的化合物均有合适的保留
● 100%水相流动相兼容
● 提供pH2-8全范围的完美峰形,方法开发简便快速
● 大幅度提高低pH条件下的柱寿命,分析成本更低
● 极低的质谱检测本底,实现高灵敏度的LC/MS分析
注意:本页面内容仅供参考,所有资料请以沃特世官方网站(www.waters.com)为准。
Atlantis T3色谱柱信息由沃特世科技(上海)有限公司(Waters)为您提供,如您想了解更多关于Atlantis T3色谱柱报价、型号、参数等信息,欢迎来电或留言咨询。
注:该产品未在中华人民共和国食品药品监督管理部门申请医疗器械注册和备案,不可用于临床诊断或治疗等相关用途
Cosmo Bio抗体,Cosmo Bio,Anti Serpin B3 (SCCA1/T4-A) and Serpin B4 (SCCA2/Leupin) pAb (Rabbit, Antiserum),CAC-SU-IZ-P04
Application: IHC, WB
Clonality: Polyclonal
Host: Rabbit
Purification: Serum
Reactivity: Human
Squamous cell carcinoma antigen (SCCA) is a member of the ovalbumin family of serine proteinase inhibitors. The protein was isolated from a metastatic cervical squamous cell carcinoma by Kato and Torigoe (1977). SCCA is detected in the superficial and intermediate layers of normal squamous epithelium, whereas the mRNA is detected in the basal and sub-basal levels. The clinical import of SCCA has been as a circulating tumor marker for squamous cell carcinoma, especially those of the cervix, head and neck, lung, and esophagus. Many clinical studies of cervical squamous cell carcinoma show that the percentage of patients with elevated circulating levels of SCCA increases from approximately 12% at stage 0 to more than 90% at stage IV. Levels fall after tumor resection and rise in approximately 90% of the patients with recurrent disease. Similar trends occur in the other types of squamous cell carcinoma, with a maximum sensitivity of approximately 60% for lung, 50% for esophageal, and 55% for head and neck tumors. The neutral form of SCCA (SCCA1, or SERPINB3) is detected in the cytoplasm of normal and some malignant squamous cells, whereas the acidic form (SCCA2, or SERPINB4) is expressed primarily in malignant cells and is the major form found in the plasma of cancer patients. Thus, the appearance of the acidic fraction of SCCA is correlated with more aggressive tumors (summary by Schneider et al., 1995). Gene expression microarray profiling analysis has identified squamous cell cancer antigen (SCCA) as an IL-13 inflammation-induced gene in tracheal epithelial cells and keratinocytes. SCCA expression is increased in asthmatic bronchiale and atopic dermatitis skin. Two isoforms of SCCA are known: SCCA1 and SCCA2. Anti-SCCA antibody is a rabbit polyclonal antibody which obtained from the immunization with purified, E. coli-derived, recombinant human SCCA2. This antibody can be used for the detection of SCCA by immunoblotting and immunostaining.
References:
1) The usefulness of combined measurements of squamous cell carcinoma antigens 1 and 2 in diagnosing atopic dermatitis. Shoichiro Ohta, et al. 2012. Ann Clin Biochem. 49: 277-284.
2) Characterization of novel squamous cell carcinoma antigen-related molecules in mice. Y. Sakata, et al. 2004. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 324(4):1340-1345.
3) The squamous cell carcinoma antigens as relevant biomarkers of atopic dermatitis. K. Mitsuishi, et al. 2005. Clin Exp Allergy 35:1327-1333.
4) Involvement of IL-32 in activation-induced cell death in T cells. Chiho Goda, et al. 2006. Int Immunol 18(2):233-240.
Cosmo Bio抗体,Cosmo Bio,Anti Aggrecan (ACAN) mAb (Clone 5D3),CAC-PRPG-AG-M02
Application: IP, ELISA, IHC(p), WB
Clonality: Monoclonal
Host: Mouse
Purification: Supernatant
Reactivity: Human, Bovine
Aggrecan is the major proteoglycan in the articular cartilage (synthesized by mature chondrocytes) and in perineuronal nets of the CNS. While its precise function around CNS neurons remains obscure, in articular cartilage it contributes to creating the hydrated gel structure of the ECM via its interaction with hyaluronan, link protein, CMPs, COMP and collagen type IX. Deletion of the aggrecan gene causes early disturbances in chondrogenesis and brain defects. Aggrecan is a multimodular molecule whose core protein is composed of three globular domains denoted G1, G2, and G3, a large extended region spanning the portion of the molecule between the globular domains G1 and G2 and containing the majority of the GAG attachment sites and a second GAG-bearing inter-globular domain (IGD) occurs between G2 and G3. The GAG attachment domain between G1 and G2 contains mainly chondroitin sulphate chains (up to 40) and some keratan sulfate chains. The inter-globular G2-G3 domain exclusively bears keratan sulphate chains. The corresponding core protein region of sclera and brain aggrecans do not seem to contain keratan sulphates. The G1 amino-terminal domain of the aggrecan core protein has the same structural motif as link protein and is responsible for the binding of the proteoglycan to hyaluronan and link protein. The G2 globular domain is homologous to the tandem repeats of G1 and of link protein and is crucial for the synthesis and cellular secretion of aggrecan. The G3 globular domain makes up the carboxyl terminus of the core protein and is similarly responsible for post-translational processing of the proteoglycan and its secretion, as well as for its molecular interactions with other cartilage ECM components. Fully glycosylated/glycanated aggrecan of articular cartilage has an average size of 2,400-2,500 kDa, but its Mr may vary with age and the conditions of the cartilage tissue. The non-glycosylated/non-glycanated core protein has an approximate Mr of 240 kDa.
References:
Virgintino D, et all., (2009) Aggrecan isoforms of perineuronal nets identify subsets of parvalbumin and calbindin neurons differentially distributed in cortical layers II-VI of human adult cortex. J. Cell. Mol. Medicine 13, 3151-3173.I161:I164.
Cosmo Bio抗体,Cosmo Bio,Anti Integrin Alpha-6 (VLA-6) mAb (Clone 537D5),CAC-PRPG-ITG-M01
Application: ICC, WB, FC, IHC(f), IF
Clonality: Monoclonal
Host: Mouse
Purification: Ascities
Reactivity: Human
Integrins are conserved, cation-dependent transmembrane receptors essential for cell survival and growth. They are comprised of α and β subunits that are differentially involved in ligand binding and connection with the cytoskeleton. They link cells to the extracellular matrix (ECM) and to cell surface-bound adhesion molecules, such as to allow cells to properly organize within tissues in relation to underlying and/or surrounding matrices. Thus, in epithelia and vasculature integrins are critical in structuring the intricate junctional complexes with underlying basement membranes, whereas in connective tissues they allow cells to form stable attachments (i.e. focal adhesions) with their surrounding interstitial matrices and rapidly convert (bidirectionally) from stationary to motile phenotypes. Integrins not engaged in ligand binding are generally dispersed on the surface of cells but tend to form microclusters. Upon ligand engagement they reorganize to form larger clusters that permit the stabilization of cell-ECM or cell-cell interactions.
Simultaneously, through phosphorylation of the cytoplasmic portion of the β subunit, integrins associate with key cytoskeletal adapter proteins, such as vinculin, talin, paxillin, tensin and FAK to activate complex signal transduction pathways converging with those elicited by growth factor receptors and other receptors for soluble and membrane-bound signal molecules. This results in the activation of the cell cycle, cell differentiation programs and/or the acquisition of motile properties. Conversely, loss of integrin binding to the matrix causes a type of programmed cell death known as anoikis. There are more than 15 α subunits and 8 β subunits, which pair with each other in different combinations to generate a repertoire of over 20 different integrin receptors. These may be selective, binding one or two ligands or promiscuous, binding multiple ligands. Similarly, the same ECM component may be recognized by one individual integrin receptor or multiple receptors. Integrin expression is frequently altered in pathological conditions and mutations in the INTG genes are associated with inheritable diseases. In cancer, integrins are fundamental in conferring a more aggressive behavior to malignant cells and are therefore considered attractive therapeutic targets. However, thus far, only one anti-integrin drug is registered for clinical application and its use is for the treatment of neurological rather neoplastic diseases.
The α6 integrin subunit pairs with two distinct β subunits, β1 and β4, and with the latter one it forms a unique integrin receptor that is essential for the assembly and maintenance of hemidesmosomes. There are a total 8 different alternatively-spliced α6 isoforms known which show a diverse tissue distribution, i.e. isoforms containing segment X1 are ubiquitously expressed, whereas isoforms containing segment X1X2 are expressed in heart, kidney, placenta, colon, duodenum, myoblasts and myotubes. Similarly, in some tissues, isoforms containing cytoplasmic segment A and isoforms containing segment B are detected while in others, only isoforms containing one cytoplasmic segment are found.